The foreign exchange market, known as forex, is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. Every day, more than six trillion dollars are exchanged as traders, banks, and institutions buy and sell currencies across the globe. Unlike stock markets that open and close each day, forex runs 24 hours a day, five days a week, offering constant opportunities.
In 2025, forex trading has become more accessible than ever. Online brokers and trading platforms allow anyone with an internet connection to open an account, practice in a demo environment, and start trading with relatively small amounts of capital.
This guide will break down what forex trading is, how the market works, and the steps to get started.
What Is Forex Trading?
Forex trading is the act of buying one currency while selling another at the same time. Every trade happens in pairs. For example, in the EUR/USD pair, the euro is the base currency and the U.S. dollar is the quote currency. If you believe the euro will rise against the dollar, you buy the pair. If you think it will fall, you sell it.
The forex market is decentralized, meaning there is no central exchange. Trades take place over-the-counter through banks, brokers, and online platforms. This structure makes forex highly liquid and available around the clock. It also gives traders access to a wide range of currency pairs.
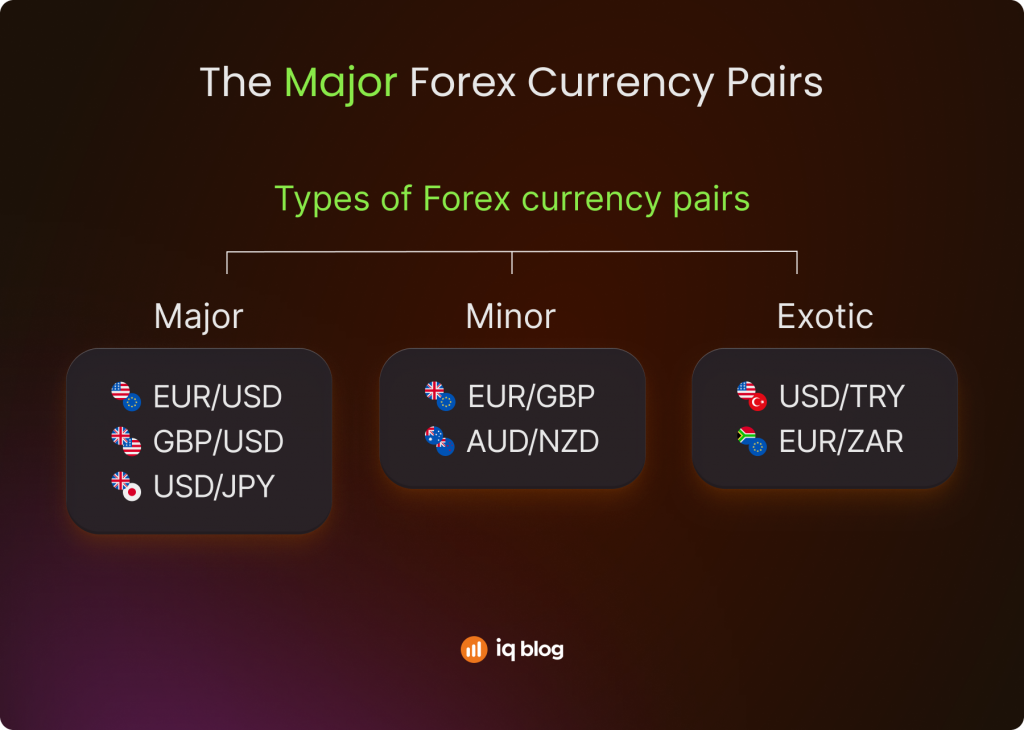
Currency pairs are divided into three main groups:
- Major pairs – The most traded, such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY. They offer high liquidity and lower spreads.
- Minor pairs – Pairs that do not include the U.S. dollar, such as EUR/GBP or AUD/NZD. They have slightly higher spreads and less liquidity.
- Exotic pairs – A major currency traded against one from a smaller or emerging economy, such as USD/TRY (Turkish lira) or EUR/ZAR (South African rand). These pairs can be volatile and carry higher transaction costs.
Forex trading is different from stock trading because traders are not investing in a company or asset long-term. Instead, they speculate on short-term price movements caused by global economic factors. This makes forex fast-paced and attractive to beginners, but also riskier if not approached with a solid understanding of the basics.
How the Forex Market Works
The forex market is unique because it is decentralized. Unlike stock markets, which operate on centralized exchanges, forex transactions take place directly between participants over the counter. Large banks, financial institutions, corporations, and retail traders all interact through a network of brokers and electronic trading platforms.
Trading is continuous, running 24 hours a day from Monday to Friday. The market is divided into major trading sessions: the Asian session, the European session, and the U.S. session. These overlaps create periods of high liquidity and strong price movements, which is when most active traders prefer to trade.
Forex prices are quoted in pairs, such as EUR/USD or GBP/JPY. The first currency is the base currency, and the second is the quote currency. The exchange rate shows how much of the quote currency is needed to buy one unit of the base. For example, if EUR/USD is 1.10, it means one euro equals 1.10 U.S. dollars.
Core Elements of Forex Trading
- Pips – The smallest unit of price movement, usually the fourth decimal place in most pairs.
- Spread – The difference between the bid and ask price. This is the cost of entering a trade.
- Leverage – Allows traders to control larger positions with smaller capital. For example, 1:30 leverage means $1,000 can control $30,000 in trades.
- Margin – The amount of capital required to open and maintain a leveraged position.
A simple example: if a trader buys EUR/USD at 1.1000 and sells at 1.1050, the 50-pip gain translates to profit, depending on position size. With leverage, even small moves like this can result in significant gains or losses, making risk management essential.
Why Trade Forex? Benefits and Risks
Forex has become one of the most attractive markets for beginners. It is open 24 hours a day, offers high liquidity, and gives access to global currencies. The same qualities that make it appealing, however, also create risks that traders must manage carefully.
Benefits of Forex
- Accessibility – Anyone with an internet connection can open an account and start trading.
- Liquidity – Trillions of dollars move daily, making it easy to enter and exit trades.
- Leverage – Control larger positions with smaller amounts of capital.
- 24/5 trading – The market never sleeps during the week, offering constant opportunities.
- Global reach – Trade major currencies like USD, EUR, and JPY, as well as emerging market pairs.
Risks of Forex
- High leverage risk – Losses can grow just as fast as profits.
- Market volatility – Prices are influenced by global news, interest rates, and politics.
- Hidden costs – Spreads, swaps, and overnight fees can reduce profits.
- Emotional pressure – Fast moves and constant access can lead to overtrading.
- Steep learning curve – Understanding pairs, strategies, and risk control takes time.
Key Forex Trading Terminology
The forex market comes with its own language. Beginners often struggle at first, but mastering the terms is essential for understanding how trades are placed and how profits or losses are measured.
A pip is the smallest unit of movement in most pairs. For EUR/USD, if the price shifts from 1.1000 to 1.1001, that is a one-pip move. A spread is the cost of trading, shown by the difference between the buying and selling price. Tighter spreads are better because they reduce entry costs.
Trades are placed in specific sizes known as lots. A standard lot equals 100,000 units of the base currency, while mini and micro lots give beginners the chance to trade smaller positions. Because these amounts are large, brokers offer leverage, which lets traders control more with less. For example, with 1:30 leverage, a deposit of $1,000 can control $30,000 in trades.
Margin is the amount you must deposit to keep a leveraged trade open. If the account falls below the margin requirement, the broker can close positions automatically. To manage risk, traders use protective orders. A stop loss closes a trade when losses reach a set level, while a take profit locks in gains once the price hits a target.
Quick Recap of Key Terms
- Pip – Smallest price move (e.g., 1.1000 to 1.1001 = 1 pip)
- Spread – Difference between buy and sell price
- Lot size – Standard 100,000 units, smaller lots for beginners
- Leverage – Control larger positions with smaller deposits
- Margin – Collateral required to open and maintain a trade
- Stop loss / Take profit – Automatic exit orders for risk and reward control
How to Start Trading Forex: Step by Step
For beginners, the biggest challenge is knowing where to start. Forex can look complex, but following a structured process makes the first steps easier. The goal is to build a safe foundation before committing real money.
Step 1: Choose a Reliable Broker
Select a regulated broker, like IQ option with transparent fees, strong security, and responsive customer support. Beginners should avoid unlicensed platforms that may pose risks.
Step 2: Open and Fund an Account
The registration process usually requires ID verification. Once approved, you can fund the account using bank transfer, card, or e-wallets. Many brokers allow small deposits to start.
Step 3: Select a Trading Platform
Most brokers offer platforms like MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, or proprietary apps such as IQ Option. A good platform provides real-time charts, easy order placement, and risk management tools.
Step 4: Learn to Read Charts
Candlestick charts are the standard in forex. Beginners should learn to spot trends, support and resistance levels, and basic price patterns before trading.
Step 5: Practice in a Demo Account
Nearly all brokers provide demo accounts funded with virtual money. Use this to test strategies and understand how trades behave without risking real capital.
Step 6: Place Your First Trade
Start small. Select a currency pair, decide whether to buy or sell, set stop loss and take profit levels, and confirm the order. Monitor the trade and review the outcome afterward.
Step 7: Build Discipline
Keep a trading journal to track what works and what does not. Review performance regularly and refine your approach before increasing trade size.
Popular Forex Trading Strategies for Beginners
Beginners often feel overwhelmed by the number of trading methods available. The key is to start with simple strategies that rely on clear rules and easy-to-spot setups. Below are four beginner-friendly approaches that form the foundation for more advanced techniques later.
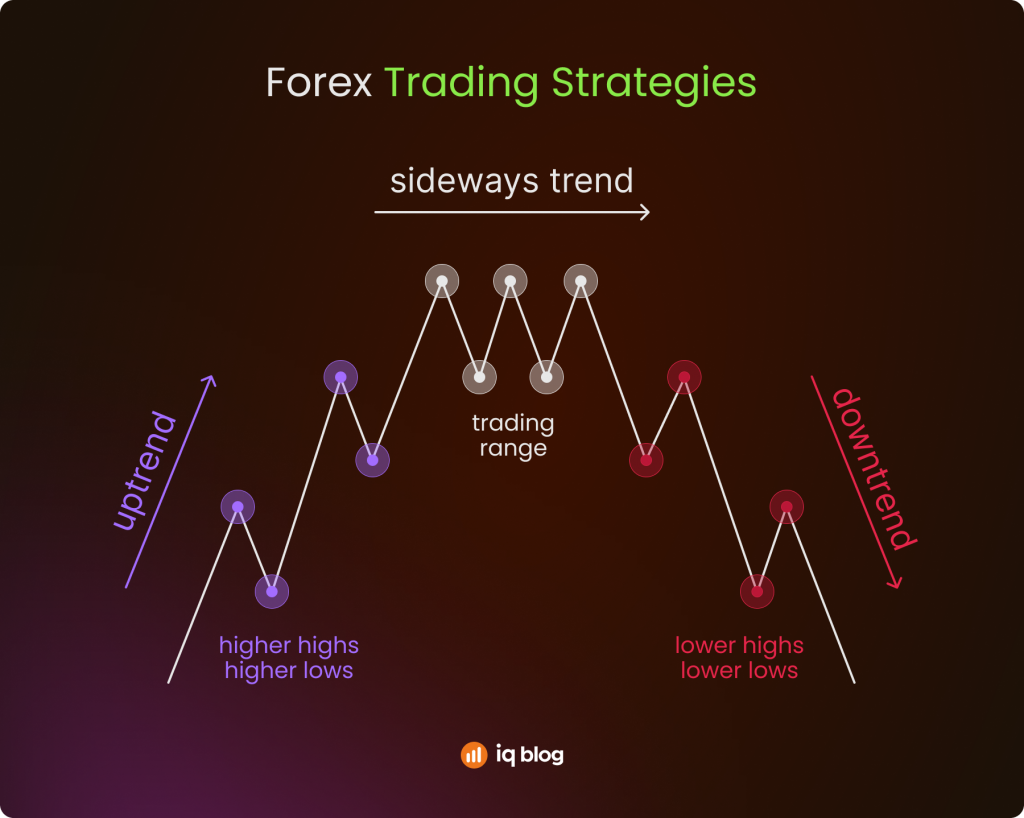
Trend-Trading
This strategy focuses on trading in the direction of the prevailing trend. If a currency pair is moving higher, beginners look for opportunities to buy; if it is falling, they look to sell. The idea is that markets tend to continue moving in the same direction for a period of time.
Traders often use moving averages to confirm the trend and enter on pullbacks. The advantage is clarity, going with the flow instead of fighting the market. The risk is that trends eventually reverse, so stop losses are essential.
Example: EUR/USD is above its 50-day moving average and making higher highs. A trader buys after a short pullback, setting a stop loss below the recent low.
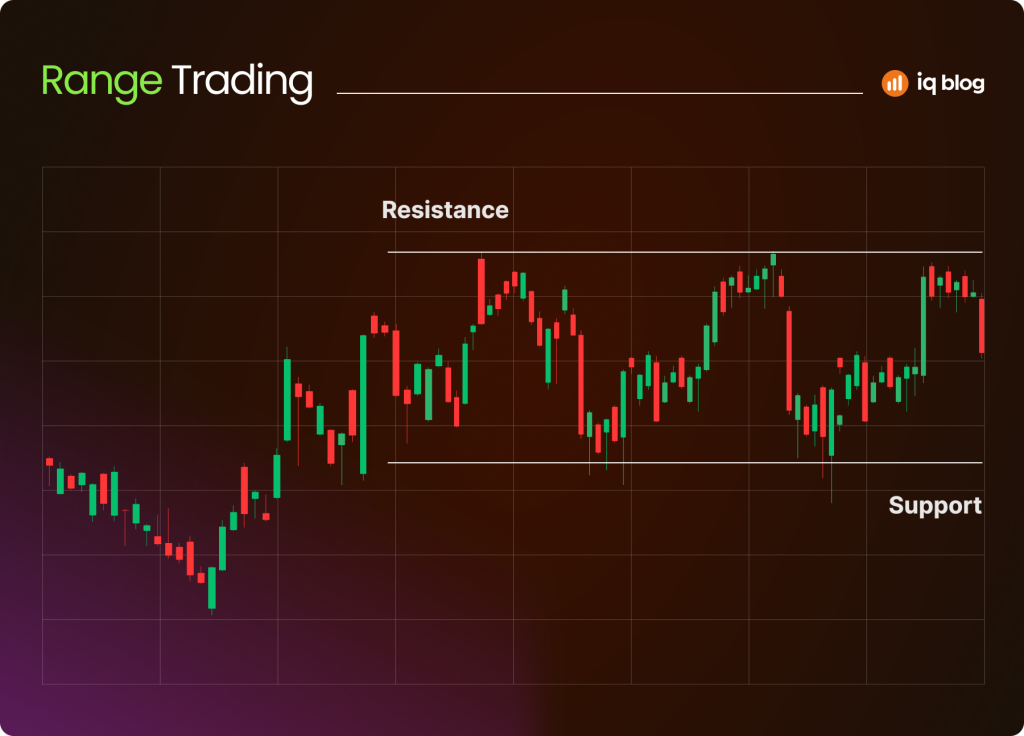
Range Trading
Range trading works when a currency pair is moving sideways between clear support and resistance levels. The goal is to buy near support and sell near resistance, capturing profits within the established range.
This method is effective in calm markets without strong trends. The main risk is that a breakout may occur, invalidating the range and hitting stop losses.
Example: GBP/USD trades between 1.2600 and 1.2800 for several days. A trader buys near 1.2600 and sells at 1.2800, repeating the process until the breakout happens.
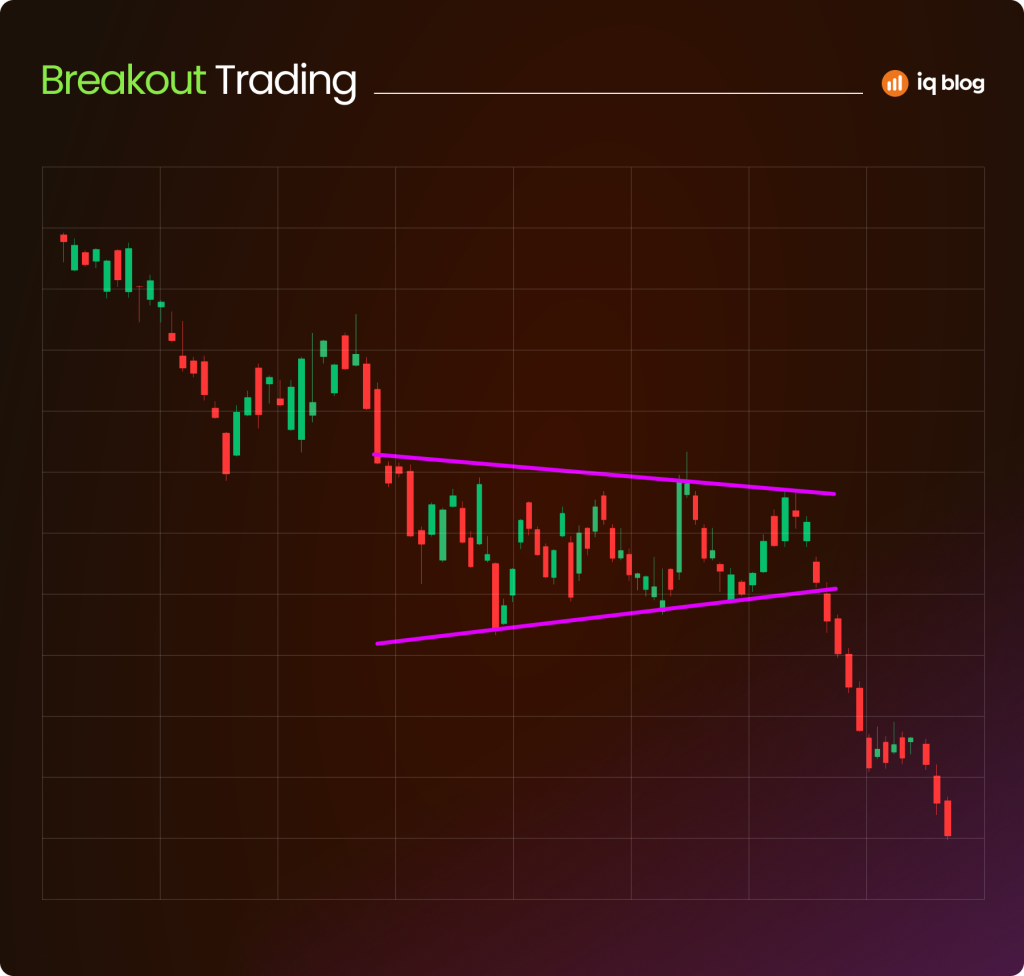
Breakout Trading
Breakout strategies aim to capture strong moves that occur when price breaks through key levels. Traders enter as soon as the breakout happens, expecting momentum to carry prices further.
The benefit is the potential for large profits when breakouts are genuine. The risk is the “false breakout,” where price briefly moves beyond a level before snapping back.
Example: USD/JPY consolidates under 150.00. When price breaks above, a trader enters long with a stop just below the breakout point.
Scalping
Scalping is a fast-paced strategy where traders make many trades throughout the day, aiming for small profits from tiny price movements. It requires discipline, quick execution, and a reliable platform.
While scalping offers many opportunities, the risks include high transaction costs and mental fatigue. Beginners should only try it once they are comfortable with basic trading mechanics.
Example: A trader buys EUR/USD, aiming for 5 pips, and exits quickly once the target is reached. The process is repeated multiple times during the session.
Risk Management in Forex
Risk management is the backbone of successful forex trading. Without it, even the best trading strategies eventually fail. The goal is not to avoid losses completely, but to keep them small enough so they never threaten the survival of the account.
One of the first rules for beginners is to manage position size. Traders should avoid committing too much capital to a single trade. A useful guideline is to risk only a small portion of the account balance per position. Stop loss orders are another essential tool, closing trades automatically once the market moves too far against you.
Core Risk Management Rules
- Keep risk per trade between 1% and 2% of account balance
- Always use stop losses to cap potential losses
- Aim for at least a 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio
Leverage deserves special attention. It allows traders to control larger positions than their deposits would normally allow, but it also magnifies losses. Many beginners make the mistake of using maximum leverage, only to see their accounts wiped out after a few losing trades. Starting with low leverage and gradually increasing it as experience grows is a safer approach.
Forex Trading in 2025: What Beginners Should Know
The forex market in 2025 is more dynamic than ever. Technology, regulation, and global economics continue to shape the way traders approach currencies. Beginners entering the market today must adapt to these changes if they want to stay competitive.
One of the biggest shifts has been the rise of AI-powered tools. Many platforms now include automated screeners, sentiment analysis, and risk calculators that help traders make faster decisions. These features, once available only to institutions, are now part of standard retail platforms. Regulation has also tightened in many regions, with leverage limits and stricter broker licensing, giving beginners more protection than in previous years.
Key Trends in 2025
- Widespread use of AI and automation in trading platforms
- Stronger regulation and reduced leverage limits for retail traders
- Growing interest in trading emerging market currencies
- Increased availability of educational content and demo accounts
For new traders, the main takeaway is that opportunities still exist, but success depends on preparation. The tools available are powerful, yet they do not replace discipline. Understanding risk, practicing in demo accounts, and keeping expectations realistic remain the cornerstones of building a long-term trading career.
Final Thoughts
Forex trading is one of the most accessible financial markets, offering beginners the chance to participate in a global system that runs around the clock. With high liquidity, low barriers to entry, and the ability to profit in both rising and falling markets, it holds strong appeal for new traders.
At the same time, forex is not simple. Leverage can turn small moves into significant gains, but it can just as easily magnify losses. The market reacts quickly to global news, interest rate changes, and political events, making preparation and risk control essential. Beginners who approach trading as a skill to be learned step by step stand a far better chance of success than those looking for quick wins.
The safest path for anyone starting in 2025 is to build knowledge, practice in demo accounts, and apply strict risk management once moving to real trades. Forex can be rewarding, but only for those who combine discipline with patience. With the right mindset, it can become not just a market to trade, but a long-term opportunity for financial growth.
FAQs: Forex Trading for Beginners
How much money do I need to start trading forex?
Many brokers allow accounts to be opened with as little as 100 – 200 USD. However, a larger balance gives more flexibility for proper risk management.
Is forex riskier than stocks?
Forex is highly liquid but also heavily influenced by leverage and global events. With high leverage, risks are greater than in stock trading, especially for beginners.
Can beginners really make money in forex?
Yes, but it takes time and discipline. Most beginners lose money at first because they trade without a plan. Practicing in a demo account and learning risk management greatly improves the chances of success.
What tools do I need to trade forex?
You need a trading platform such as MetaTrader or IQ Option, access to real-time charts, an economic calendar, and a reliable internet connection. Risk calculators and journaling tools are also recommended.
When is the best time to trade forex?
The most active times are when major sessions overlap, such as London – New York. These hours bring the highest liquidity and the strongest price moves.

