It is here: a brand new trading engine that allows for a new way of Forex trading. How does Forex on margin work and how may traders experience this instrument to the fullest? In this article, we will be covering all the necessary points to explain how to trade on the margin balance, how to open deals, what the new features are and, generally, what the benefits and risks of this type of trading are.
First of all, let us explain the basics of how margin trading works and explore the new terms that are unique to this type of trading.
What is Forex on margin trading?
The main idea of trading with margin is the ability to trade with an amount of money larger than the initial deposit a trader has. The concept is similar to the traditional loan system that banks provide to individuals who wish to make a purchase, the cost of which exceeds their own savings.
For instance, if you wish to buy an apartment, you may contact the bank and they will provide you with a mortgage. You pay the downpayment, but the rest of the funds are covered by the bank. In this scenario, the apartment will be the collateral until the debt is repaid. Similarly, in margin trading, the broker provides you with leverage, which allows you to trade with a larger investment amount. This increases the possible positive outcome, however, at the same time it increases the risk and losses.
Leverage
The concept of leverage is not much different from the more familiar “multiplier” that has been traditionally used on the platform. To better understand how leverage works, let’s look at the example:
A trader invests $50 of their own money in a deal and chooses a leverage of 1:20. This means that for every $1 that the trader invests, the broker will add $20 to help increase the position size. This way, the trader operates with not just $50, but with $50* 20 = $1000. Accordingly, the returns for the deal will be calculated based on the investment of $1000, making a much higher return possible for the trader.
It is important to note that higher leverage trading makes the trades riskier, as it also increases the size of the loss, should the trader predict the direction of price development inaccurately.
What are the features of Forex on margin trading?
The trade room looks familiar, however it has many new features, crucial for margin trading. Let’s briefly go over every section to see what it is used for and how to choose deal settings correctly.
Quantity
Looking at the right sidebar of the trade room, the first setting to choose is the “Quantity”, which is essentially the amount of the asset that a trader chooses to trade. The quantity is measured in lots. In Forex, lot size will determine how much of the base currency a trader will buy or sell. 1 standard lot = 100,000 units of base currency. A trader may choose smaller amounts, for example, a nano-lot (0,001 lot), micro-lot (0,01 lot) or a mini-lot (0,1 lot).
For example, when a trader chooses to trade the quantity of 0.1 on EUR/USD, it means that they are willing to buy or sell 1,000 EUR. A quantity of 0.003 would mean 300 EUR and so on.
Pip value
The next point that is reflected in the menu is the pip value. One pip represents the fourth digit after coma in the asset price. It shows the cost of the smallest price change in the asset for the trader. The value of a pip depends on the chosen quantity of the asset: the higher the quantity, the higher the pip value is going to be.
Margin
Trader’s own money required for the deal is called margin. This is the downpayment that the broker freezes on your balance — it is not deducted from you immediately, but simply held until the deal is executed. The margin amount is always calculated in base currency.
It is important to note that the trader does not choose the amount of margin: it gets calculated automatically. It will correlate with the leverage you choose — higher leverage would mean lower margin as more of the broker’s funds are used. Lower leverage would require a higher amount of trader’s own funds. The minimum margin requirement is 0.2% of trade size. Should you like to double check the margin size, you may use the following formula:
Margin = Lot size * Contract size / Leverage
In this formula, contract size always equals 1 lot (100,000 units of base currency). For example, If a trader is using 1:20 leverage to trade 0.01 lots, their margin will equal the following:
0.01 * 100,000 / 20 = 50 USD
Take Profit/ Stop Loss
As per usual, the money management tools that a trader can use are Take Profit and Stop Loss, however, they are set in pips, relative to the “Ask” or “Bid” price at which the deal is opened. These levels can be adjusted, added or removed completely at any moment while the deal is running.
How to trade Forex on margin?
In order to open a deal, a trader may follow the steps below:
- Choose an asset from the list of assets.
- Choose the quantity of the asset you wish to trade. The quantity should be higher than 0.001 lots.
- The quantity of the asset traded will set the required margin. Make sure you have sufficient balance to execute the deal.
- Set the Take Profit and Stop Loss levels in order to manage the losses.
- Decide on the direction which the price will develop in and click “Buy” or “Sell” accordingly.
- You may check the ongoing deal in your portfolio and close it at any moment.
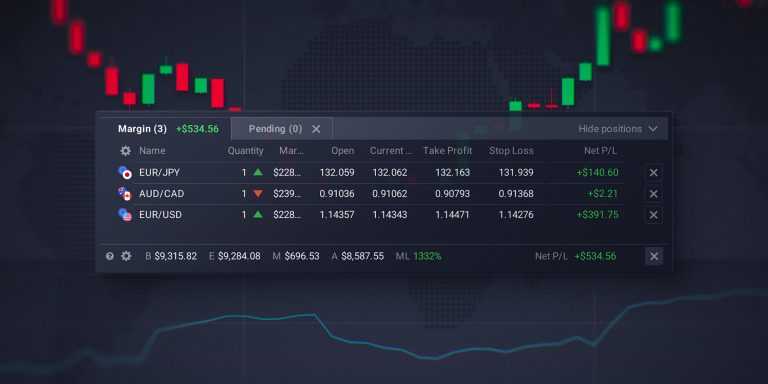
Total portfolio
To check the ongoing deals that you have on your account, click the “total portfolio” button. The tab will display all the active and pending orders, the asset, type of instrument, date, quantity, opening price and TP/SL specifications. The specifications do not disrupt the chart, which means that you can view the charts and your portfolio at the same time to have better control over it.
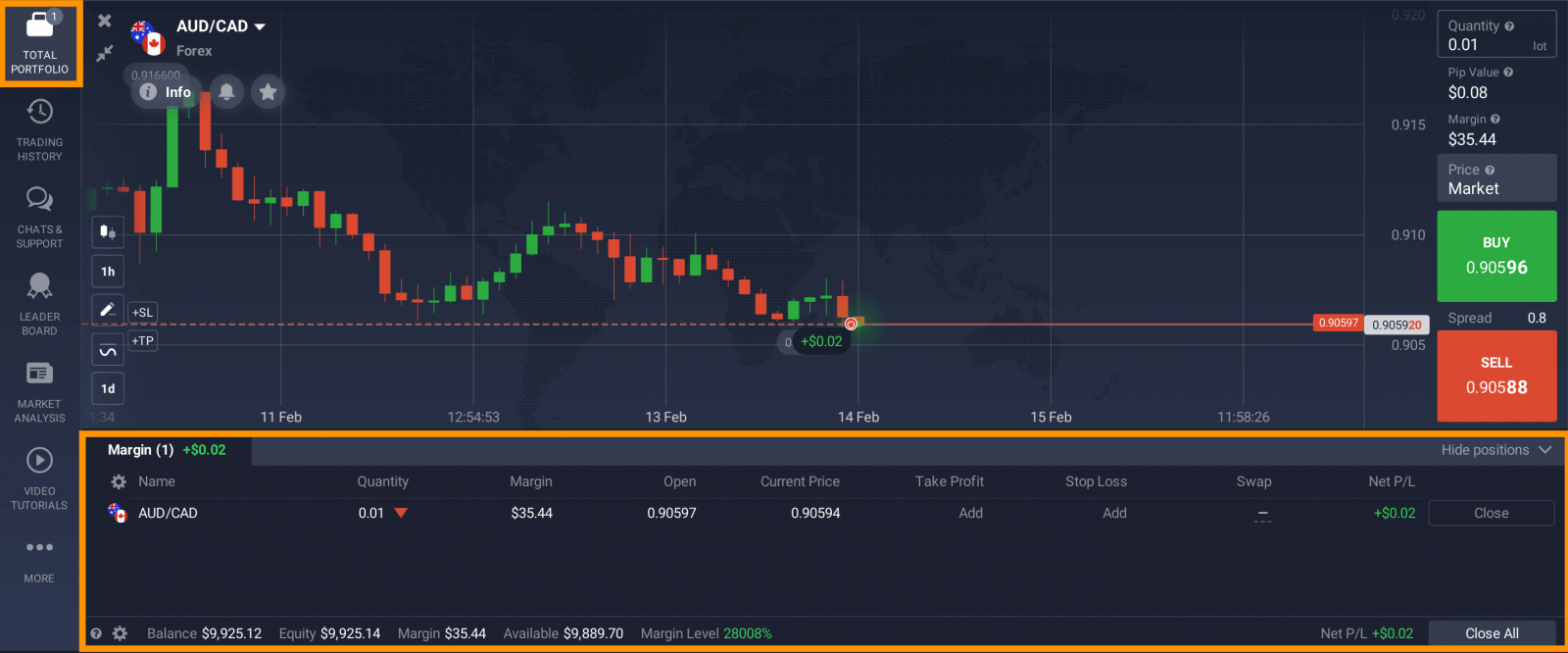
Balance information
The forex on margin trading balance has seen several changes to the way it is displayed. Now, besides the balance amount, one can view the equity of their account, current profit or loss, the margin level and the amount of available funds. Each section reflects an important metric of a trader’s account:
Margin level — shows the influence of the currently opened positions on the trader’s account. If the margin level falls to 100%, the trader cannot open any new positions, until they increase their margin level by closing the positions or topping up the balance. The red line indicates a 50% margin level: if it is reached, the opened positions will be closed automatically.
Equity — this is the total portfolio of the trader, including the profit or loss from the currently ongoing deal. It is a dynamic value, which will change according to the current results of open deals.
Balance — unlike equity, balance does not include this dynamic data and simply reflects the amount of funds on balance.
Margin — shows the amount of “frozen” funds on the trader’s balance, which the broker is holding until the deals are closed.
Net P/L — reflects the profit or loss amount of all deals on the margin engine.
Available — the amount of funds that the trader can currently use to open new deals or withdraw.
Conclusion
Forex on margin is an opportunity for traders to open deals with a position size larger than trader’s own funds. Traders can monitor the equity of their balance to understand how much loss or profit they are dealing with. Current deals can be tracked in the “total portfolio” section. As there are many features available, forex on margin trading may be useful both for experienced traders and for those who are just learning about Forex.